Present European meals manufacturing will not be sustainable in the long run. Fossil and mineral sources are depleted. Altering local weather is resulting in elevated drought eventson the one hand and extra heavy rainfall then again. Additionally the ever-increasing world inhabitants results in an elevated meals demand. The transition in the direction of a round agro-food system, slightly than present non-circular manufacturing provide chains, is an inevitable step in the direction of rising sustainability, respecting the planetary boundaries. In any respect phases of meals manufacturing, distribution and consumption, stakeholders comparable to scientists, coverage makers, farmers, meals producers, shoppers are re-thinking and re-designing the present meals manufacturing approaches. The European Fee has set formidable targets beneath the European Inexperienced Deal of which the New Round Financial system Motion Plan (CEAP)1 and the Farm to Fork technique2 are the principle constructing blocks. They embody the discount of using synthetic fertilizers, discount of nutrient and meals losses, progress of natural farming, water reuse, and so forth. At each stage (farm stage, meals provide chain stage, client stage) and in any respect scales (native, regional, world) modifications are at present going down and lots of extra future modifications are anticipated. The transition in the direction of a round meals system is a systemic change, and it’s anticipated that the manufacturing of meals in 10–20 years from now might be considerably totally different from present approaches.
Not too long ago, Muscat et al.3 proposed 5 ecological rules (safeguard, keep away from, prioritize, recycle and entropy) to information biomass use in the direction of a round bioeconomy. Contemplating utility of those rules, extreme modifications within the European meals manufacturing system are to be anticipated and – in response to latest opinions4,5—these might associate with the prevalence of potential new meals security dangers. Three of those rules are prone to influence meals security. Examples are given right here.
Safeguard – This precept prevents the depletion of pure sources and thus bans using synthetic fertilizers. Together with an anticipated lowering variety of livestock in Europe, and thus availability of manure, this ends in a requirement for different merchandise to supply the required vitamins for agricultural apply. These vitamins are vastly out there in merchandise we at present think about as being waste, comparable to sewage sludge. Thus, sewage sludge is an attention-grabbing candidate for future use for agricultural utility (most probably after remedy). The reintroduction of such a product could also be accompanied with the introduction of an entire vary of legacy and new chemical hazards, e.g., human prescribed drugs, private care merchandise and contaminants like heavy metals, plant safety merchandise and protracted natural pollution (POPs), together with per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs).
Prioritize – This precept states that merchandise must be used as excessive within the meals chain as attainable. Thus, if a product is suited to human meals, it must be used as such and never as animal feed. Because of this, decrease high quality merchandise might be out there for, as an illustration, animal feed. Using decrease high quality merchandise at larger ranges within the meals chain might pose new meals security hazards. Moreover, new processing strategies to upcycle co-products, right here outlined as by-products from manufacturing processes, may also induce new meals security hazards.
Recycle – This precept focusses on the reuse of merchandise in meals manufacturing which are at present being thought-about as waste. A transparent result’s that extra co-products and waste streams are recycled and launched in e.g., animal feed or compost. The reintroduction of such merchandise can yield new meals security hazards. An instance is the elevated use of intra- or inter-species of animal co-products. Using processed animal proteins from mammals in feed of cattle may transmit prions inflicting bovine spongiform encephalopathy (BSE). Additionally, low concentrations of contaminants could be reintroduced as these co-products are solely to a minor extent systemically monitored.
Evidently, new meals security challenges come up within the transition to extra round meals manufacturing. Laws will not be in all circumstances fit-for-purpose for a round meals manufacturing system. In some circumstances regulation hampers the transition, in different circumstances the rules will not be absolutely designed to forestall new meals issues of safety from occurring. Regulation 2020/7416 was carried out just lately, however solely focuses on measures for secure utility from a microbiological hazards perspective, however not for chemical hazards. The principle meals security dangers appear to originate from the (re)introduction of low(er) high quality merchandise or merchandise which are at present thought-about waste into the meals system4,5. On this perspective paper, we current a simplified threat evaluation and administration method, based mostly on HACCP rules, consisting of 5 questions. We select to begin from the HACCP method since HACCP is already largely utilized in an operational setting by meals and feed stakeholders (from manufacturing to distribution). We now have adopted the HACCP method for assessing meals security in a round meals manufacturing system and with aiming to determine data gaps therein. Along with feed/meals producers, it may be utilized by scientists/technologists designing new round processes, and by threat assessors/managers who want to decide potential dangers of latest improvement in round meals & feed manufacturing. The effectiveness of this novel method is demonstrated based mostly on two at present related case research associated to round meals manufacturing to determine important data gaps, spotlight factors of concern and assess present boundaries.
Strategy
5 query method
To asses meals security within the transition to a round meals manufacturing system, we right here suggest an efficient method that enables detection of important data gaps. This method is predicated on 5 features that must be addressed; components touched upon by these 5 questions are additionally lined by the EU laws of the Normal Meals Regulation7 and HACCP approaches. In conventional threat evaluation (that are available in numerous approaches8,9, the principle steps are (1) hazard identification, (2) hazard characterization, (3) publicity evaluation and (4) threat characterization. These steps had been the premise of the introduced method, but extra consideration is given to the publicity evaluation. Extra particularly, this pertains to the enter of by-products within the round system and the conduct of the hazards within the round food-production system. The 5 questions are proven in Fig. 1.
1: Enter—decide which (waste) materials or co-product is used within the round meals manufacturing system. 2: Hazards—determine the hazards that happen within the round meals manufacturing system. 3: Destiny—decide how do these hazards transfer via the round meals manufacturing system. 4: Dangers—decide the dangers of those hazards within the round meals manufacturing system. 5: Acceptability—decide if the danger is appropriate or if threat administration measures must be taken. Copyright Bureau voor Beeldzaken, 2022.
Q1: Enter offers with defining the case and may contain the next features: What uncooked supplies and co-products are integrated within the manufacturing and distribution course of? The place do they arrive from? Right here, the dimensions of the method must also be thought-about. Does the method think about a single farm, a area or the entire nation or planet? Small scale processes can result in very amplified dangers for a selected area. Giant scale processes may doubtlessly hurt a big group of shoppers.
Q2: Hazard offers with the identification and definition of the (un)anticipated hazards: What potential hazards could be current in these uncooked supplies and co-products? Is laws out there? Can and can an enter management monitoring technique be utilized? Monitoring information are required to sufficiently reply this query.
Hazards could be divided into three varieties: chemical, organic and bodily. Chemical hazards might embody chemical compounds, comparable to (heavy) metals, plant safety merchandise, prescribed drugs (for animals and people), pure toxins (mycotoxins, plant toxins, marine toxins), environmental contaminants (dioxins, polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs), PFASs) and course of contaminants (e.g., mineral oil saturated hydrocarbons (MOSH) and mineral oil fragrant hydrocarbons (MOAH). Organic hazards embody all organisms, like micro organism, and protozoa, in addition to biologically energetic particles comparable to prions and viruses, that may be dangerous to human well being. Bodily hazards are as an illustration (micro)plastics, metallic particles and bone fragments, in addition to radioactive particles.
Hazards can originate from two totally different sources: (1) hazards which are deliberately utilized in meals manufacturing (so known as ‘residues’) and hazards that (2) unintentionally (and generally unknowingly) are launched into the meals system (‘contaminants’). The deliberately utilized hazards embody prescribed drugs and plant safety merchandise. Hazards which are unintendedly launched normally originate from co-products of any type or environmental contamination.
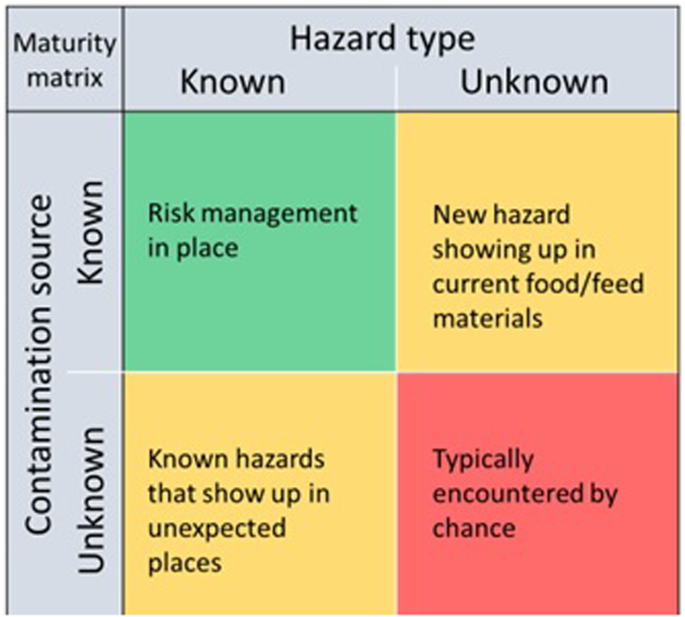
The various kinds of hazards might have a unique nature, and the extent of data and regulation differs considerably. For instance, ‘recognized’ hazards might seem in sudden locations, whereas in different circumstances ‘unknown’ hazards might present up in recognized circumstances. Determine 2 exhibits a categorization of knowns and unknowns as regards the character and the origin of the hazard. An extra rationalization is given beneath.
Prime-left: recognized hazards present up in recognized meals/feed manufacturing conditions; top-right: in recognized meals/feed manufacturing conditions beforehand unknown hazards present up; bottom-left: in beforehand unknown meals/feed manufacturing conditions recognized hazards present up; bottom-right: in beforehand unknown meals/feed manufacturing conditions beforehand unknown hazards present up. See textual content for rationalization and examples.
Recognized hazards from recognized sources are quite a few. These embody, however will not be restricted to, marine toxins in shellfish, veterinary medicines in animal co-products and plant safety merchandise in animal feed. For recognized hazards from recognized sources, sometimes applicable threat administration practices are in place. Authorized most limits, comparable to laid down for instance in Fee Regulation 2023/91510 (succession of regulation EC/1881/2006), different limits and management packages are in place and are constantly reviewed based mostly on the most recent scientific insights.
A case of a recognized hazard arising from an unknown supply because of recycling was the case of medroxyprogesterone acetate (MPA) scandal within the early 2000s. A glycose containing co-product originating from the manufacturing of birth-control remedy was utilized in pig feed. In numerous pigs infertility was recognized. Solely then it was discovered that the animal feed contained excessive concentrations of MPA, a substance that’s banned in Europe for animal remedy. Hundreds of animals had been destructed11. For this case, one may advocate that the co-product was per definition a high-risk product that had been launched into the meals system.
An instance of an unknown hazard originating from a recognized supply is properly illustrated by the case of mineral oil saturated hydrocarbons (MOSH) and mineral oil fragrant hydrocarbons (MOAH) in recycled paper and carton board used as meals contact materials. Though it’s recognized that (recycled) meals contact supplies might comprise sure contaminants12, the presence of MOSH/MOAH in recycled paper and carton board was lengthy uncared for. This difficulty was found already within the early 2010s13,14, nevertheless it was propelled solely after a non-governmental group (NGO) introduced this to better public consideration. This resulted in a number of measures on the meals producer facet and authorities to adequately determine and handle dangers, in the end resulting in discount of the dietary publicity to those contaminants.
Essentially the most intriguing class is the class with unknown hazards in a but unknown state of affairs. An instance of such a case developed from 2006 onwards in Germany, the place the applying of per- and polyfluoralkyl substances (PFAS) polluted soil conditioners led to a widespread PFAS contamination within the catchment areas of the rivers Moehne and Higher-Ruhr. By that point, there was solely little recognized in regards to the hazards of PFASs (unknown hazard), and the prevalence in soil conditioners (unknown state of affairs), which resulted in an uncontrolled air pollution occasion. Due to the uncertainty, drastic measures had been carried out to scale back undesirable human publicity of residents within the impacted space. Later, an analogous occasion occurred within the south of Germany (Rastatt space)15,16,17.
Q3: Destiny offers with the translocation and persistence of the meals security hazards. For the translocation it entails the next features: Do the hazards keep within the compartment (e.g., animal, soil, crop, water) they’re launched into or do they transfer amongst compartments? In that case, to which compartments? It is very important perceive how hazards transfer amongst compartments from a mechanistic perspective. The destiny of a hazard is dependent upon particular circumstances, together with the properties of the contaminant and the setting the contaminant is in. For example, the transmission of contaminants from soil to water is dependent upon the soil composition, but in addition on the kind of contaminant itselve18.
Concerning the persistence: are the hazards degraded to a no-effect focus by the system (pure mitigation) or are they persistent, or reworked to different bioactive hazards? In a super state of affairs, a hazard is mitigated by the system itself, e.g., a substance is degraded/deactivated in soil. The persistence of a hazard must be often called it is a vital parameter in understanding the destiny. Persistent hazards, e.g., DDT or microplastics, stay within the system and may accumulate. If these hazards at present present no unfavorable results, they could achieve this in time, whether or not that’s in 5 or 100 years from now. Information must be obtained and must be made publicly out there to permit a significant threat evaluation. Word that degradation of, as an illustration, a chemical hazard can lead to the transformation of the hazard, nonetheless (or much more) exerting a unfavorable impact. An instance is estradiol, a feminine hormone, that may be reworked in soil to the transformation product estrone, a extra estrogenic substance19. Wastewater remedy may additionally lead to different transformation merchandise that present (eco)toxicological potential20,21,22. Word that some hazards can exert an acute threat (e.g., allergens in meals merchandise) and as such their diploma of persistence is subordinate.
This fall: Threat evaluation offers with the quantification or estimation of the danger and entails questions comparable to: Do the hazards yield a possible threat (one well being perspective) within the compartments they will happen in? Threat research can’t be carried out for all hazards, in all compartments for all attainable toxicological endpoints. Subsequently, you will need to perceive which hazards could be current during which compartment. As such, threat research ought to deal with particular hazards in particular compartments for particular endpoints. To complicate threat evaluation, particularly in a round meals manufacturing system, mixtures of hazards can happen, which want particular consideration.
Q5: Threat administration offers with all of the features of threat administration, and entails questions like: Are such potential dangers permissible (from a coverage and client perspective) and may such potential dangers be actively mitigated, ideally on the supply? Right here additionally the potential interplay amongst hazards must be thought-about, e.g., how the publicity to chemical contaminants can lead to a better influence of a microbial an infection.
Utility and data gaps
To get a greater understanding of the complexity of the subject and to determine data gaps utilizing the introduced method, the method is utilized to 2 totally different circumstances with a deal with unknown and recognized organic and chemical hazards.
Case 1: Former foodstuffs to animal feed
As a substitute of going to waste, former foodstuffs are more and more being utilized in animal feed. Within the EU, yearly 5 million tonnes of former foodstuffs are already getting used for feed23. Till now, merchandise of primarily plant origin are being valorized at a big scale into animal feed. The foodstuffs which are at present getting used are merchandise that in precept are/had been additionally appropriate for human consumption, however might not be offered as such (anymore), comparable to chopping stays, leftovers from product improvement, merchandise over expiry date, or different merchandise that don’t meet the standard requirements established. Assortment and conversion of former foodstuffs into feed is in Europe coordinated by a couple of massive processing corporations, having devoted suppliers, that course of these merchandise into feed merchandise. These processes are actually restricted to comparatively secure former foodstuffs originating from bakeries and confectionery factories however from a sustainability perspective, in addition to with the intention to tackle the rising want for proteins, reuse of foodstuffs of animal origin, comparable to milk, eggs, and meat that for some purpose will not be appropriate (anymore) for human consumption (e.g., due to business causes, high quality, manufacturing failures and so forth.), must be thought-about along with the present plant-based supplies.
Strict EU laws for using animal proteins as animal feed is in place for the reason that begin of the twenty first century with the intention to achieve management over the unfold of BSE in addition to the unfold of sure contagious animal illnesses in Europe. These embody three forms of restrictions being: (a) the ruminant ban (protein of ruminants will not be allowed to be used as feed), (b) the prolonged feed ban (animal proteins might not be utilized in a number of different purposes), and (c) the species to species ban (anti-cannibalism; proteins from one species might not be fed to the identical species). Although some exemptions are in place, these rules to a big extent hamper using animal derived proteins as animal feed. About twenty years later, the European Fee is contemplating some a rest of the prolonged feed ban to allow a extra round manufacturing system. Since August 2021, processed pig proteins are allowed for use as hen feed, and processed hen proteins are allowed to be used in pig feed, and eight insect species are at present allowed for inclusion in animal feed (EC 2021/1372)24.
An extra rest might be to permit utilizing so-called swill (kitchen refuse/waste) in feed. These waste streams are generated in each family, however for logistical causes, solely (bigger) kitchens and caterers are thought-about practical sources. The method with the 5 questions will assist to determine the threats and alternatives.
Q1: Enter: Former foodstuffs, significantly swill (kitchen refuse/waste) for animal feed. Major supply for these waste streams are (bigger) eating places and caterers. Assortment and processing will sometimes be organized at a neighborhood or regional scale.
Q2: Hazard: The first hazards related to swill are biologically energetic particles (prions; BSE/TSE) and pathogens/zoonoses (e.g., foot and mouth illness, Aujeszky’s illness, African swine flu)25,26. Swill not solely has the danger of transmitting animal illnesses, but in addition illnesses that ultimately can have an effect on human beings, comparable to Creutzfeld-Jacob illness, a uncommon spongiform encephalitis (mind illness), suspected to be attributable to consumption of BSE-infected beef. For these causes, present EU laws doesn’t enable inclusion of swill in animal feed27. Additionally for that purpose monitoring packages for forbidden anima proteins in animal feed are in place.
Q3: Destiny: The reuse of swill bears the danger of introducing novel hazards into the animal manufacturing chain26,28. Such hazards might flow into and/or accumulate within the meals system. Viruses and prions could also be re-introduced by way of swill and should unfold amongst animals and switch from animals to people. Notably prions are notoriously proof against digestive enzymes, warmth, disinfectants and desiccation and strongly bind to solids comparable to feed or soil particles. Certain to particles, prions can keep infectious for a few years and should as such stay current as a hazard within the system. Lack of correct elimination mechanisms might even result in accumulation within the meals chain.
This fall: Threat: As a result of number of sources and processing choices, a real threat evaluation can solely be carried out on a case-by-case foundation. It’s apparent that animal proteins inside swill at present bear unacceptable dangers. A complicating issue right here is that in lots of present kitchen and catering practices, all swill (each plant and animal based mostly) is disposed as combined waste. Which means that the combination carries a bigger threat than a few of its particular person constituents would. For instance, fruit and vegetable waste, which generally is the most important a part of swill, bears zero-risk for transmitting animal-related organic hazards. Nevertheless, from a precautionary precept, as soon as in a mix with extra hazardous animal waste, the entire combination must be handled as excessive threat materials. Would plant-based swill be collected individually, this may be simpler to reuse in animal feed and human meals.
Q5: Threat administration: The present ban on swill utility in animal feed has been a really efficient measure to scale back attainable well being dangers to a minimal. Nevertheless, in view of the present ambition to scale back meals waste and shut manufacturing loops, different choices to make the most of swill must be explored. This requires enough threat governance approaches.
Information gaps. This case pertains to a recognized hazard in a recognized situation (Q2, Fig. 2). The applying of our proposed method reveals that present laws is efficient in decreasing dangers to an absolute minimal. For animal proteins, laws has confirmed to be efficient: between 2005 and 2015 about 73,000,000 cattle had been examined for BSE within the EU, and on this interval the variety of reported circumstances dropped from 554 circumstances in 2005 to simply two in 201529.
Nevertheless, present EU laws hampers the additional utilization of former foodstuffs comparable to swill on a bigger scale. From a meals safety perspective, different choices must be investigated.
Rest of the established feed bans ought to due to this fact be accompanied by case-based threat assessments carried out on intensive scientific foundation, as has been achieved previous to the latest partial carry of the prolonged feed ban30. Such an method ought to allow to make knowledgeable choices on acceptable dangers, though this will solely be achieved for recognized hazards and recognized sources.
We conclude that, for the case of the reintroduction of swill into the meals manufacturing chain, data gaps are primarily associated to threat administration (Q5). Decreasing potential dangers of swill begins with higher separation on the supply. A promising begin might be to discover the choices of comparatively clear streams inside the catering waste.
As evident from the difficulties concerned with combined waste streams talked about earlier than, separation of swill into fractions with larger (e.g., meat, bones) or decrease dangers (e.g., fruit & greens, fries, bread) might be an choice to handle these dangers extra exactly. It’s not clear but to what extent such a separation could be achieved in apply. The sensible points concerning separation and assortment must be additional explored.
One other step could be the investigation of probably the most promising routes in the direction of valorization, comparable to to permit its use for sure devoted functions comparable to feeding it to specific animals (together with bugs), conversion into microbial proteins (fermentation) or breakdown into precious elements (biorefinery).
Case 2: Water reuse as a water supply in irrigation in agriculture
Wastewater merchandise comprise a collection of supplies originating from city and industrial wastewater remedy vegetation (WWTP). City and industrial wastewater is, subsequent to being a waste stream, additionally a precious supply of recent water and vitamins. When mentioning wastewater right here, we additionally think about grey water and excreta31. The European Fee (EC) goals at rising the reuse of handled wastewater from a present 3% to fifteen% in a few years32 with the intention to battle freshwater shortages. Wastewater mining offers with the reuse of wastewater merchandise, e.g., reclaimed water, sludge, struvite and different supplies that are precious merchandise thereof. Agriculture is a vital (future) recipient of wastewater merchandise for the aim of irrigation and fertilization. Nations and areas just like the state of California, Spain and Israel are missing adequate sources of freshwater already and face drought points incessantly and even (semi)constantly. They’ve turned to reclaimed water for irrigation of lawns and public gardens (California) or agricultural manufacturing fields (e.g., Spain, Israel). Wastewater is understood to be susceptible to comprise numerous pathogens and chemical hazards, and these might comprise dangers when agricultural reuse is taken into account. The secure reuse of reclaimed water for agricultural irrigation from a microbiological hazards perspective was just lately regulated6,33. Right here, we restrict the evaluation to the chemical hazards of wastewater reuse. Contemplating its nature, a plethora of chemical compounds happen in wastewater8,34,35, generally known as contaminants of rising concern (CEC). These embody pharmaceutical merchandise (e.g., ache relievers, blood stress drugs, anticonvulsant remedy, antibiotics), private care merchandise (e.g., detergents like quaternary ammonium compounds and musk fragrances like galaxolide), coloring brokers from textiles (e.g., indigo dyes), industrial merchandise (e.g., PFASs), plant safety merchandise and family chemical compounds. These contaminants, when current in reclaimed water, might current potential hazards when utilized in agriculture for irrigation. On this respect, it might compromise the security of meals merchandise. Some research have demonstrated the uptake and deposition of contaminants from reclaimed water into crops, comparable to residues of prescribed drugs in greens36,37,38 and PFAS in vegetation39,40. One might understand that the prevalence of such contaminants would a priori rule out using reclaimed water. However given the intrinsic worth when it comes to water and vitamins, it’s essential to analyze if, and the way reclaimed water could be utilized in agriculture offering secure meals.Not too long ago printed laws and tips6,33 supplies standards for utility of reclaimed water. Nevertheless, these standards focus primarily microbiological hazards, though it’s acknowledged that enormous data gaps exist on the danger of CECs in agricultural produce.
The 5 query method is posed for the case of water reuse utilizing reclaimed water for irrigation functions to determine important data gaps. Nevertheless, because the quantity and number of hazards on this case could be very massive, this can’t be achieved briefly. Moreover, for a lot of hazards inadequate information are at present out there for an enough evaluation. To reveal the applicability of the introduced method, we restricted the scope of this case to the potential presence of PFAS in wastewater. Although, word that this solely covers a small a part of the potential dangers.
Q1: Enter: The intention is to extend using reclaimed water from home origin for irrigation on a worldwide scale. Presently reclaimed water is utilized for irrigation in particular nations41, however not but on a worldwide scale.
Q2: Hazard: Many various microbiological, pathogenic or chemical hazards could be current in (handled) wastewater. Some are recognized and others are sudden and unknown. Regardless that the sudden hazards want consideration, right here we deal with a recognized one. Subsequently, the main target is on chemical hazards solely, and particularly on PFASs. This group of chemical compounds comprises over hundreds of gear of which, in response to present data, a restricted quantity, together with perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) and perfluorooctanoic sulfonate (PFOS), are thought-about probably the most related.
Q3: Destiny: Some research investigated the destiny of PFASs in WWTP water42,43. Present wastewater remedy is insufficiently efficient for full elimination of PFASs. Consequently, PFASs stay within the reclaimedwater. When making use of this water on agricultural land, the PFASs might be in direct contact with the crops and/or be combined with the topsoil. Relying on the PFASs traits and soil composition, the PFASs can (1) adsorb to soil, immobilizing the PFAS44, (2) leach to floor and/or floor water45,46, (3) run-off or leach in a rainfall occasion or (4) be taken up by crops39,40. Presently the extent to which they could be taken up by crops will not be properly understood however this course of clearly is dependent upon the physico-chemical traits of the PFASs, on the soil traits and on the crop species and/or selection39,40. When taken up by crops, the PFASs might find yourself in animal feed or human meals. Additionally, PFASs that leach to floor water may, relying on their physical-chemical properties, accumulate in fish47, via which people could be uncovered. Presently, information and fashions to foretell the destiny of the person PFASs after land utility will not be out there. Particularly the perfluoroalkyl carboxylic acids and perfluoroalkyl sulfonic acids (e.g., PFOS and PFOA) are recognized to be very persistent. They won’t degrade beneath pure situations and as such accumulate in soils and meals. Moreover, a latest examine confirmed that PFASs precursors, e.g., 8:2 fluorotelomer sulfonic acid, can partly be reworked to legacy PFASs like PFOA throughout wastewater remedy including to the PFASs burden.
This fall: Threat: PFASs are deemed to exert a unfavorable well being impact at extraordinarily low concentrations. The present state of data is that a number of PFASs have, amongst different well being results, a unfavorable impact on the immune system48, and present human dietary exposures within the EU result in unacceptable dangers48. This suggests that the publicity to PFAS may lead to an elevated susceptibility for microbial infections in animals and people. Results of PFASs on soil and aquatic life ecosystems are vastly unknown.
Q5: Threat administration: With the present data, growing threat administration, together with components like threat mitigation and threat monitoring is wise to do. Mitigation could be of technological or regulatory nature.
Information gaps. This case is expounded to a largely recognized hazard in an unknown state of affairs (Q2, Fig. 2), when particularly scoped to PFASs. Nevertheless, in a broader perspective, it pertains to unknown hazards in an unknown state of affairs (Fig. 2) as the character of all related PFASs when reusing wastewater in meals manufacturing is at present not properly understood.
As regards the present regulatory instruments, tips on minimal necessities for water reuse had been just lately adopted6,33, setting uniform minimal water high quality necessities for the secure reuse of reclaimed water in agricultural irrigation. Nevertheless, these tips significantly cope with a secure utility of wastewater with a deal with viral and microbiological dangers. Some instructions are given on assess destiny and dangers of contaminants, although in a generic method. However, the present meals security laws setting most limits (MLs) (e.g., 2023/915) solely describes recognized chemical compounds in recognized conditions and is due to this fact not geared up to deal with new contaminants in unknown conditions. Some stories have indicated no or little threat is to be anticipated of their discipline circumstances studied36,49,50, which is promising. Nevertheless, that is removed from a complete understanding of dangers within the range of crops, range of reclaimed water and variety of agricultural manufacturing approaches. There may be thus a necessity for a regulatory framework that helps a secure utility of reclaimed water that additionally addresses chemical contaminants.
From the applying of the 5 query method, for a secure utility of reclaimed water in meals manufacturing, a number of data gaps exist. These are associated to the hazard (Q2), the destiny (Q3), the danger (This fall) and the danger administration (Q5).
With regard to the hazard identification (Q2), the data gaps embody the character (identification) of contaminants in wastewater and the variation of contaminant ranges (seasonal, batch-to-batch and between WWTPs). On this regard a number of research reported on the identification and focus ranges of PFAS and different contaminants in (handled) wastewater51,52,53, however a considerable and systematic data base is missing. For a lot of chemical compounds and bodily hazards, solely scarce info is at present out there, significantly on reclaimed water supposed for agricultural use.
With reference to the destiny (Q3), data gaps relate to the transmission of hazards amongst compartments, for instance, to soil, crops and meals or feed, making an allowance for the variation of those compartments (e.g., soil composition). For a lot of hazards, present data on the persistence and transmission of contaminants amongst compartments (e.g., mobility), is proscribed. Since it isn’t attainable to check the destiny of all chemical compounds in all circumstances, the last word intention is to derive fashions that enable to estimate the persistence and switch to totally different compartments in numerous eventualities. When such a data base is out there, stakeholders could make related selections as in the direction of what wastewater merchandise can be utilized for what crops, and may rank probably the most pressing dangers. This prioritization is urgently required to check the precise threat of hazards for people, animals and the ecosystem upon publicity to the related concentrations of the hazards.
When contemplating PFAS, with regard to the danger (This fall) solely restricted info is out there. Some research reveal a unfavorable impact on the human immune system, however these research centered on PFOA and PFOS solely. No or very restricted info is out there on all different PFAS which hampers the implementation of efficient laws. Moreover, consequential dangers, like a better susceptibility for a microbial an infection, are unknown.
As well as, technological developments are wanted that assist the elimination of contaminants from wastewater merchandise (Q5), or ideally, stop contaminants from being disposed into wastewater. One other mitigation technique is the monitoring of reclaimed water previous to utility, ideally by a easy and on-site relevant methodology. To what diploma these, and doubtlessly different mitigation methods, are price efficient stays to be decided.
A manner ahead
Meals techniques reaching the planetary boundaries have led to the emergence of formidable plans for decreasing the influence on the planet. Circularity in meals manufacturing can contribute considerably to reaching these targets. The transition to extra sustainable meals manufacturing is pressing. In terms of circularity in meals manufacturing, meals security is a prerequisite for societal acceptance of those processes. Within the above described two circumstances, we spotlight that there are a number of data gaps, technical challenges and regulatory hurdles, or missing rules, that must be resolved. Hurdles might counteract a well timed transition to a extra round meals manufacturing. Right here we talk about attainable options to this. A significant problem lies within the velocity of transition versus cautious and secure adaptation of processes. The dialogue is especially centered on attainable options that allow a well timed transition. This boils all the way down to accumulating related info, but in addition simplifying methods to characterize hazards, destiny and dangers.
As regards enter (Q1), a greater understanding is required of the sources of co-products that may be valorized into meals and feed manufacturing (case 1). Additionally info on composition, high quality and security of co-products and waste merchandise is required. This can facilitate a greater route in the direction of some extent of use within the meals manufacturing chain. In that respect, a separated assortment on the supply may also allow a extra particular use (straight utilizable, or after a biorefining step). The place present rules prohibit use of such co-products (e.g., within the case of swill), the leverage of such regulation might stimulate the valorization of such merchandise, as soon as it has turn out to be clear that these streams can be utilized in a secure manner. Monitoring of co-products for a variety of recognized hazards is urgently wanted. As regards case 2, a greater understanding is required of the wastewater merchandise that will, after remedy, be used for irrigation or fertilization functions.
As regards hazards (Q2), the present system for figuring out chemical hazards is usually based mostly on a substance-by-substance foundation. The best way ahead right here is in a number of instructions. Chemical hazards must be regarded within the mixtures as they’re related for publicity. Furthermore, the rise of sturdy analytical measurement methodologies (e.g., excessive decision mass spectrometry) reveal that publicity to a plethora of contaminants, degradation merchandise and metabolites takes place concurrently. Willpower of all particular person chemical, organic and bodily hazards is unrealistic as it’s useful resource and time-consuming. Prioritization of hazard evaluation is required to maneuver ahead, in addition to multi analytical strategies that may decide a spread of contaminants in a pattern on the time. The dearth of pure chemical requirements additional complicates this case. Subsequently methods like read-across, in-silico hazard dedication and in-vitro hazard dedication must turn out to be accepted methodologies, additionally from a regulatory perspective54,55,56.
Regarding destiny (Q3), there’s a want to know the round meals manufacturing techniques as an entire. Lipophilic contaminants (e.g., dioxins) will observe the circulation of the lipids in a meals system, which permits for fast assessments the place potential contaminants accumulate in a meals system. It turns into extra complicated with chemical hazards that are intermediately lipophilic or water soluble and cell, as these might find yourself in numerous compartments within the meals chain and ecosystem. There’s a clear want for a fast and straightforward evaluation of the destiny and persistence of contaminants (together with uptake by crops, bugs and animals), based mostly on fashions that describe the related meals manufacturing chains and compartments. Such fashions enable a fast evaluation of the destiny of the hazard in a temporal and spatial style. It is very important recognize information on microbial, enzymatic, chemical and bodily degradation as it might relieve attainable hazards. In case extra quantitative information are wanted, such information must be gathered via devoted experiments. The supply of highly effective analytical strategies supplies a wealth of knowledge on the prevalence of recognized and unknown compounds (e.g., non-target screening & identification), and this will speed up our understanding of the destiny of contaminants. A generic mannequin method permits for an preliminary evaluation of the destiny, even when no identification or hazard of a substance has been assessed.
As regards dangers (This fall), threat evaluation has historically been based mostly on a substance-by-substance foundation. Given the massive variety of contaminants (e.g., PFASs), degradation merchandise and metabolites, this calls for various approaches that combine a number of contaminants on the similar time, e.g., by wanting on the antagonistic impact of teams of contaminants (combination toxicity), by taking a look at sure physical-chemical properties of the compound(s) (quantitative structure-activity relationship = QSAR) or just by taking consultant marker contaminants that symbolize an entire class of compounds. New evaluation strategies (NAMs) might present potentialities to evaluate bigger numbers of contaminants on the similar time. Nevertheless, taking such approaches will result in a better stage of uncertainty within the estimated threat, than the normal substance-by-substance method. In lots of circumstances, it’s seemingly that there’s adequate margin to ensure security. In different circumstances, a necessity will emerge to scale back the uncertainty to get a extra correct estimation of the danger.
Threat administration (Q5) is a really broad subject, that offers with improvement of meals security threat mitigation measures, monitoring, compliance testing and so forth. It’s out of the scope of this paper to extensively talk about attainable options. Briefly, rules which have come into drive up to now to guard shoppers now hamper progress of the well timed transition in the direction of sustainable meals manufacturing (case 1). However, an absence of a transparent regulatory framework might hamper adaptation of latest practices. For instance, the shortage of instructions on cope with particularly chemical contaminants in reclaimed water (case 2) in relation to meals security when used for irrigation might stop such water reuse. Moreover, the transition to a round meals manufacturing system would profit from cross-cutting approaches between various kinds of laws together with environmental, meals security, agricultural and well being rules. Such horizontal approaches must be based mostly on high quality protocols which set out ‘finish of waste’ standards for manufacturing as is now proposed within the revision of the Waste Framework Directive57.
Acknowledging the truth that rules can’t be modified in a single day, and that many stakeholders depend on present rules, we pledge for re-evaluation of the meals security regulatory framework. Other than regulatory features, there may be additionally the side of acceptable threat: how a lot threat is appropriate for the stakeholders and society? There are promising strategies and metrics to check dangers of assorted varieties, comparable to disability-adjusted life years (DALY)58. These approaches might assist in the general analysis and comparability of various meals security eventualities. The dialogue above centered on choices to take away boundaries for a speedy transition. Different viewpoints may additionally be related within the dialogue. Ultimately it’s a part of the coverage making course of to stability these viewpoints.
Concluding remarks
The transition in the direction of a round agro-food system is a vital contributor to enhance the sustainability of our meals manufacturing system. How can we stop using agrochemicals (e.g., plant safety merchandise and veterinary medication) in meals manufacturing? And if these are required, how will we stop accumulation and re-circulation of such contaminants within the ecosystem affecting aquatic and terrestrial biota well being and soil well being? Can biomass that was beforehand not utilized for human meals or animal feed be used as such with out introducing a well being hazard? And does using different sources or the reintroduction of co-products additionally reintroduce undesirable contaminants into the system? And may they accumulate? These are essential safety-related features that have to be thought-about within the present transition in the direction of round meals manufacturing techniques. These concerns assist to forestall new security associated well being dangers, however in addition they contribute to the progressive and secure utility of at present undervalued co-products, comparable to sewage sludge, swill and reclaimed water.
In present meals manufacturing techniques many meals security hazards are understood and managed. It’s anticipated that new hazards will seem or accumulate, resulting in new -and much less understood- meals security dangers within the round meals manufacturing system. The present system of identification of hazards and the administration thereof will not be well-designed to assist the quick transition to round meals manufacturing techniques, which are anticipated to return quickly over the following 5–15 years. Arriving at consensus if a sure contaminant is hazardous, and designing applicable threat administration measures might take 5–15 years of scientific, societal and political debate and evaluation. Given the variety of (potential) pathogens and chemical compounds of commerce, that is unacceptably lengthy. We imagine there must be a stability between a speedy transition and the security of our meals techniques. Threat ‘acceptance’ (a part of Q5) is, due to this fact, extraordinarily related.
To evaluate, information and speed up the security evaluation of round meals manufacturing processes, a easy method consisting of 5 questions is introduced, complementing the commonly accepted HACCP system. We pose that, although the questions are simple, they’re at present tough to reply in lots of circumstances as a result of we lack the data to take action. Utilizing this method, we’ve recognized data gaps and regulatory hurdles that must be resolved. Within the transition to a round economic system, threat evaluation and administration ought to emphasize extra on the publicity to sudden (with regard to its nature and its origin) and mixtures of hazards, as hazards may flow into and accumulate within the meals manufacturing system. Additionally we observe that extra information on the prevalence and destiny of hazards and the event of fashions are required to adequately carry out threat evaluation in a round meals manufacturing system. Final, new methods of valorisation of co-products are required during which a safe-by-design method must be adopted.